Behaviour Based Robotics
This article talks about the basics of behaviour based robotics and shows some examples
Have you ever wondered why we humans survived the race of evolution amongst all the other creatures that inhabited Earth millions of years ago?
It is because of our intelligence and ability to acclimatize to a changing environment. Similarly, the idea of robots operating in response to their environment was proposed in the late eighties. This was known as Behavior-Oriented Artificial Intelligence.
In that era, robots were designed to do labor-intensive tasks and the term artificial intelligence was limited to robots executing specific sets of instructions on their own which were already fed to their system at the time of design which was previously known as ‘classical AI’. This common approach towards robotics changed over course of time when the need for robots started to arise not only to do labor-intensive tasks but to also perform complex tasks where humans cannot reach, for example exploring the depth of Earth or cleaning difficult to reach sewage blocks. This led to the current development in the definition of AI and furthered the idea of Behavior-Based Robotics.
Behaviour-Based Robotics, or BBR can be defined as an approach in robotics that focuses on robots that can exhibit complex appearing behaviors despite little internal variable states to model its immediate environment and gradually correct its actions via sensory-motor links. This definition might seem daunting at the beginning but it is quite straightforward to understand and is explained further.
Behavior-based robots respond to their external stimuli which enables them to avoid obstacles and complete their tasks. For example, if a robot is supposed to deliver some instrument in a particular hospital room. Mapping the whole structure of a hospital is not beneficial as it will keep changing according to real-time situations and there might be too much crowd for the robot to move in a previously empty room, that is why mapping a small area in its environment enables the robot to work efficiently and also enables the robot to have less complex instruction set as it has to only implement actions like wandering, obstacle avoiding and delivering the package while classical AI-Based robot will have to include mapped environment of the hospital and have to find the best path according to the map which might not work in a real-time scenario.
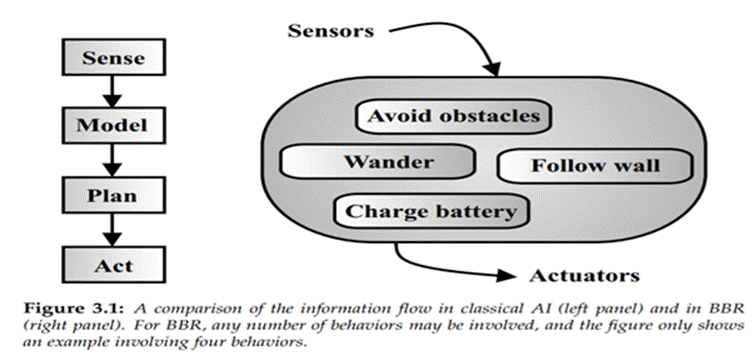
Classical AI Approach
The figure above illustrates the classical AI approach which focuses on planning out the course of actions beforehand and then doing the actual task while the figure below illustrates a behavior-based approach that is doing the basic actions like wandering, obstacle avoiding, etc. by actuators from information sensed from its external environment.
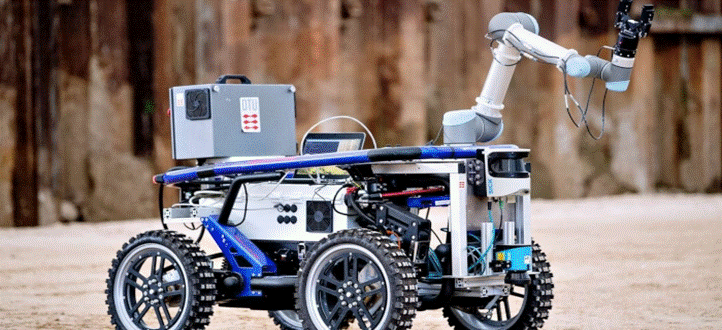
Behaviour Based Robot for Obstcale Avoidance
This huge advantage of adaptability and less complexity has made BBR popular. Some features of behavior-based robots are mentioned below:
- Autonomous: behavior-based robots are highly autonomous, that is they are not dependent much on human instructions for executing their task.
- Mechanically Imprecise: Classic AI-based robots need to be mechanically precisely shaped as all instructions which are to be executed are given to robots taking into account their precise shape. Behavior-based Robots do not require precise shape since they are adaptable to their environment. This enables us to design robots using BBR at a cheaper cost and less weight.
- Less Computational Resources: Computational Resources are less in robots designed using BBR as discussed in the example at the beginning of the article.
- Improving through Learning: Robots designed using BBR can improve through learning which enables them to cope up with the surprises they might face in their tasks.
- Software can be Reused: Behavior-based Robots rely more on types of sensors and motors connected to them than a concrete structure which enables us to port low-level code from one robot to another.
- Integrated into an Environment: Behavior-based robots are not seen as isolated devices but as a part of their environment due to their adaptability. Behavior-based Robots tend to be more natural in their behaviors (i.e., their movements). Just like an animal behaves as an integrated part of its surroundings, behavior-based robots behave as a part of their integrated environment.
Along with these features, Behavior-based Robots need to prioritize their tasks to ensure that their survival or the survival of their target is ensured. To achieve this, Behavior-based Robots are first equipped with the most fundamental of all behaviors, that deal with their survival. At work, these robots can prioritize their tasks according to the situations they face. For example, if a robot faces an issue of low battery, then its priority task should be to find a nearby charging station even if it makes it move apart from its main goal as the robot should remain functional throughout the task to complete it. In some scenarios, a robot has to sacrifice itself to protect a human being in case of bomb-defusing robots or if it can cause damage to some other things like important artificial satellites while exploring space.
Behavior-based Robotics has its key feature adaptation which we have observed from a variety of living species around us for many generations. That is why designs of Behavior-based Robots are inspired by biological structures of different species(biologically inspired) or their behaviors(ethologically inspired). These Behavior-based Robots have a wide range of applications that are used in practical applications as well as in futuristic exploratory endeavors. Some of the standard examples of Behavior-based Robotics are Obstacle avoidance, navigation, terrain mapping, chasing/pursuit, object manipulation, task division, and cooperation. Even the Mars rover ‘Sojourner’ is designed to autonomously explore the surface of Mars and analyze its environment. The current advancement in Behavior-based robotics has enabled us to have the following robots:
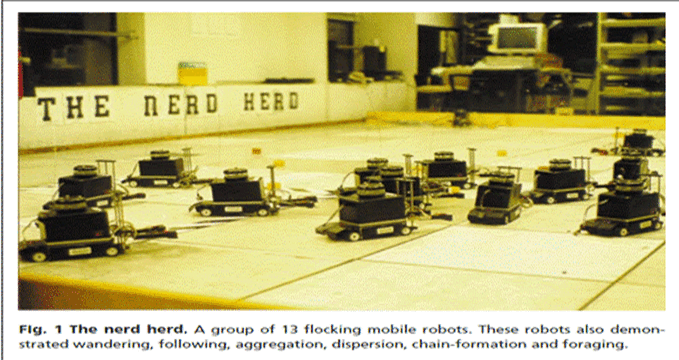
Robots inspired by observing equivalent behavior of ants, chimps, chickens, etc. But not physically structured like those species(ethologically inspired).


Biologically inspired robots with a structure resembling fish for aquatic locomotion and a structure resembling a bat for terrestrial locomotion.
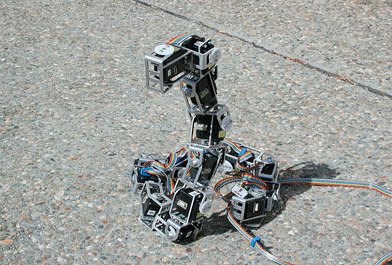
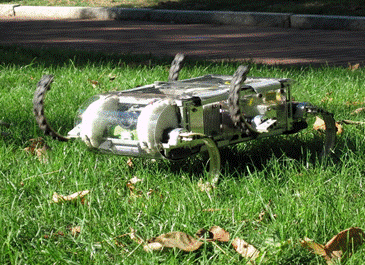
Snake-bot for limbless locomotion and six-legged hexapod robot inspired from cockroach locomotion.
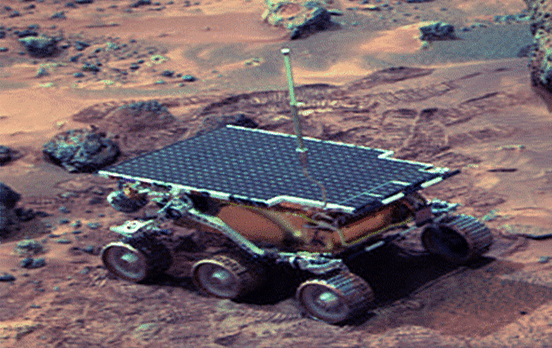
Behavior-based Mars Rover ‘Sojourner’ Currently, research is going on to develop fully autonomous robots and extend the intelligence of these robots to the intelligence of the human brain.

Some disadvantages or inefficiencies associated with BBR:
- Despite having research going on in the field of BBR, the robots made using this technology are showing intelligence not more than insect level intelligence which is not even close to the intelligence and complexity of the human brain.
- Classical AI-Based robots are more efficient than the BBR in an environment which doesn’t change in real-time or in case tasks to be performed are repetitive like robots used in the manufacturing industry where the same task is to be repeated daily. In these cases, it is convenient to feed all the information to the robot beforehand which can help to perform the tasks easily.
Conclusion
Behavior-based Robotics is a rapidly growing field because of its special feature of adaptability. Behavior-Based Robots can be used to perform tasks that human beings can’t like exploring space or analyzing the surfaces of planets in our solar system. This field has immense potential and breakthroughs will be witnessed soon via various research projects that are underway.
References
If you want to explore the concept of Behavior-Based Robotics in more detail and technical terms, you can refer to these links or textbooks
-
Arkin Ronald C. “Behavior Based Robotics”. The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts,1998.
-
Mataric Maja J. “Behavior-based robotics as a tool for synthesis of artificial behavior and analysis of natural behavior”. Trends in Cognitive Sciences – Vol. 2, No. 3, March 1998
-
NASA gives MIT a humanoid robot to develop software for future space missions